- Have any questions?
- +86 15953537010
- admin@wepower-electronic.com
- Home
- Tempereaure Measurement
- Temperature Thermometer
- Gas-actuated Thermometer
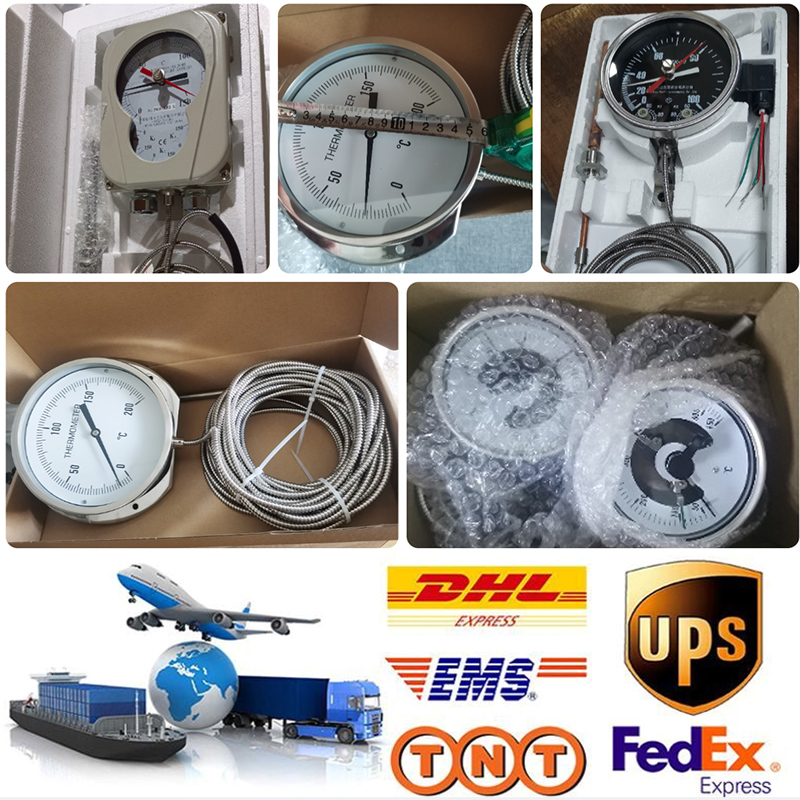
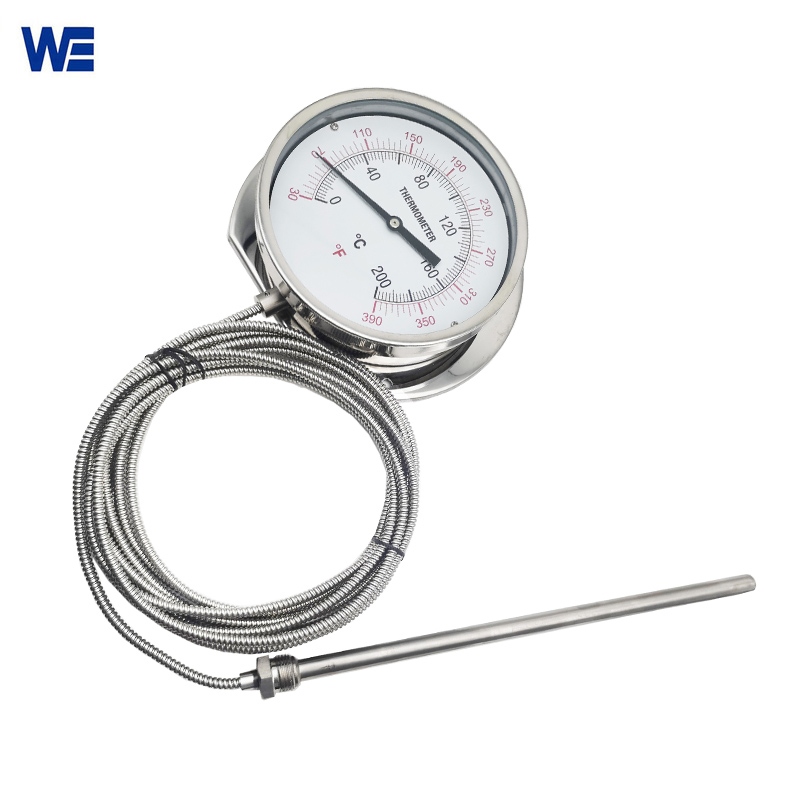
Gas-actuated Thermometer
Gas-actuated thermometers require little upkeep and are simple to install and operate. Another benefit of this expansion thermometer is its quick response time, which makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications requiring quick temperature readings.
![]()
Gas-actuated Thermometers require little upkeep and are simple to install and operate. Another benefit of this gas-actuated thermometer is its quick response time, which makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications requiring quick temperature readings.
What’s The Working Principle Of Gas-actuated Thermometer?
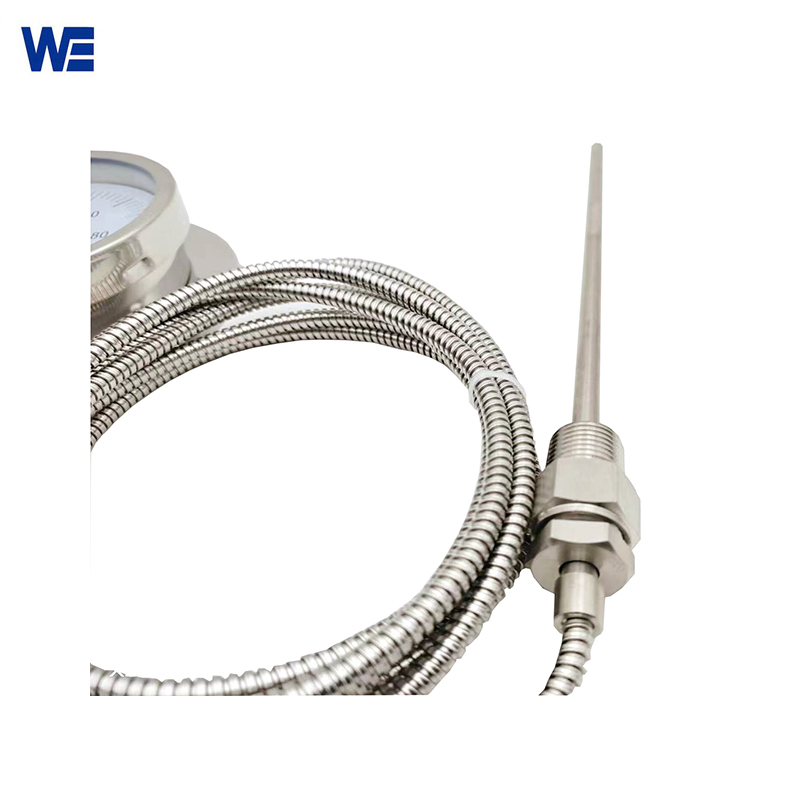
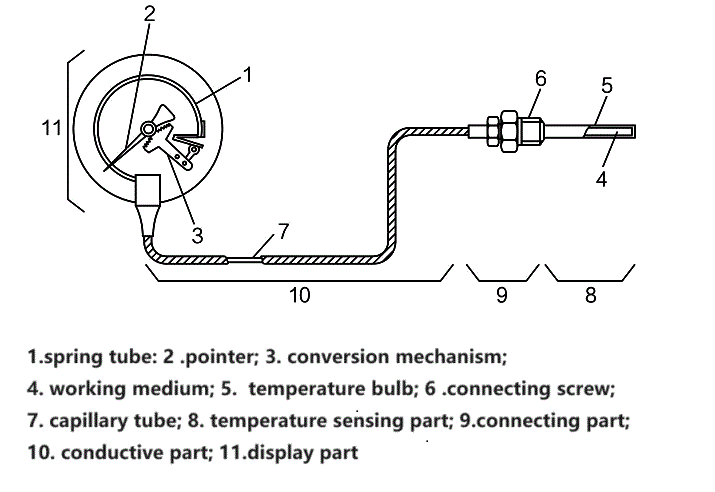
A metal component (i.e., a filled temperature sensing system) including a temperature bulb filled with temperature sensing medium, a capillary tube for pressure transfer, and a spring tube for pressure sensitivity makes up a Gas-actuated Thermometer. The temperature bulb contains a gas, liquid, evaporating liquid, etc. as the temperature-sensing medium.
The temperature bulb is inserted into the medium to be tested in order to measure the temperature. The temperature rise causes the working medium in the temperature bulb to expand, which raises the pressure. With the aid of gears, levers, and other transmission mechanisms, the pointer rotates to display the relevant temperature when the pressure change is sent to the spring tube via the capillary tube and causes it to flex somewhat.
Advantages Of Gas-actuated Thermometer:
- Wide temperature range, can accurately measure extremely high or low temperatures.
- It is not affected by electrical interference or fluctuations and remains reliable in harsh environments.
- Easy to install and use, with minimal maintenance requirements.
- Quick response, fast temperature measurement.
Parameters:
| Product Name | Remote Expansion Thermometer |
| Temperature Range | -30…+60,0….100,0…120,0…160,0…200,0…300,0…350,0…400,0..500,0…600 |
| Material | stainless steel 304/316 |
| Accuracy | 1.5% of range |
| Diameter of Dial Indicator | φ100mm;150mm;75mm;63mm |
| Capillary Material | SS304/SS316 |
| Probe Diameter | φ6, φ10, φ12 |
| Process connecting Method | Without fixedMovable thread outer
Movable thread inner Fixed thread Fixed flange Adjustable thread Adjustable flange |
| Thread | M16X1.5; M27X2; G1/2; G3/4,M33×2 |
| Direction | Axial/Radial |
| Contact Type(for electric contact type): | NO,NC,NONO,NCNC,NONC,NCNO,SPDT |
![]()
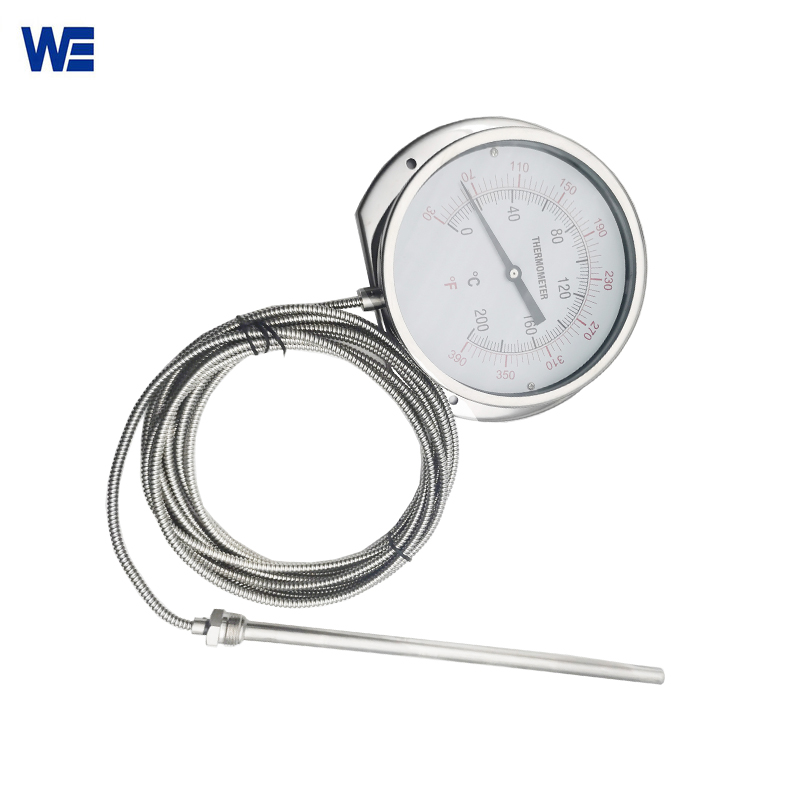


Diagram:
![]()


![]()















